According to world statistics, about 80% of the adult population of our vast planet is united by the same health problem - periodically, or even continuously, back pain in the lumbar region. Back pain is the main symptom of many diseases of the spine and internal organs located in the abdominal cavity. And it is really in vain that most of those who experience discomfort in this area, bypassing the doctor and not understanding the reasons, begin to intensively use various ointments and other "home lotions". With this method, you can easily achieve the opposite of the expected result.
Reason: specify, not included
The success of any treatment directly depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis, with the elimination of perceived symptoms, the likelihood of relapse increases. After that, such treatment can only worsen the situation. Therefore, first of all, you need to carefully check the condition of all organs, the symptoms of which may be pain in the lumbar region.
Digestive system
The severity of diseases of the digestive system (pancreatitis, ulcers, colitis, cholecystitis, enteritis, appendicitis) often causes pain in the lumbar region.
urinary system
Often, kidney pain is mistaken for a symptom of lumbar spine disease, because its nature is the same. Diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract of various etiologies are accompanied not only by "recoil" to the lower back, but also by urinary disturbances (increased frequency, discomfort, the presence of blood in the urine and its turbidity), and an increase in body temperature.
reproductive system
With problems with reproductive organs in men and women in the acute stage, pain often radiates to the lumbar region, tailbone or to the side. The nature of this pain is often girdle without clear localization.
If any organ disease that is not associated with the musculoskeletal system is detected, it is he who is treated, because he is the real cause of the pain syndrome. If, after a thorough examination, problems with the above organs are not identified, then most likely the problem is with the spine.
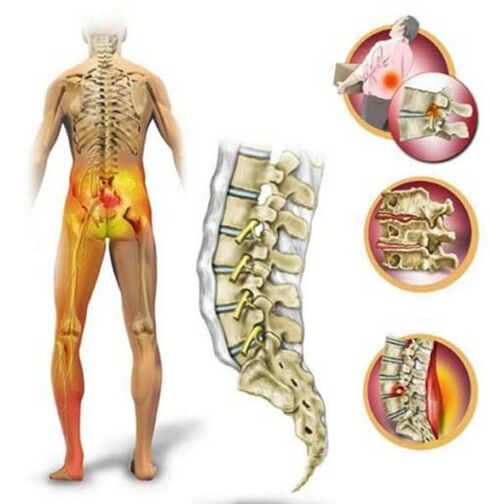
Osteochondrosis
The most mobile part of the spine, which takes the largest part of the load, is the lumbosacral. With an inactive lifestyle, excessive stress and insufficient intake of nutrients into the cartilage tissue of the spine, degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral cartilage in the lumbar region occur - osteochondrosis.
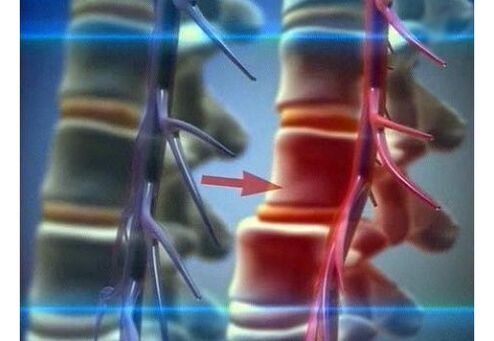
Symptoms and stages of the disease
The main worrying symptom of osteochondrosis is pain in the lumbar region. At the initial stage, it is localized and directed to the sacrum, its character is attractive (painful). During this period, the destruction process affects the nucleus pulposus (dehydration occurs), as well as the vertebral disc (standing height decreases). Discomfort is observed with heavy loads, and the pain itself is mild.
After some time, if the problem is ignored and no measures are taken, the shooting starts in the thighs and buttocks. Due to the narrowing of the intervertebral space, the muscles and ligaments "sag" and the spine becomes unstable. This leads to loss of sensation and numbness.
The third stage is characterized by morphological changes in the disc, the spine itself is severely deformed, disc protrusion and prolapse develop. The pain at this stage becomes more intense and prolonged. Every movement brought unbearable pain. It is possible to squeeze the area of the spinal cord, canals and nerve endings adjacent to the pain point due to the fact that the fibrous ring protrudes and affects the spinal canal.
The last stage of lumbar osteochondrosis "forces" the body to adapt to the changes that have occurred as a result of the disease in the following way. In order for support and protection functions to be preserved, bone tissue grows in diseased areas. This usually leads to various microtraumas, and then to deformities.
A comprehensive approach to treatment
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis must be comprehensive, regardless of the stage of development of the disease. With a mild form, the treatment prognosis is good, the deformation process can be completely stopped and the consequences minimized. At the final stage of the disease, the task of treatment is to eliminate all symptoms and consequences, normalize the nutrition of the spinal tissue, strengthen the muscular corset of the entire back and its lower part in particular.
Medicines
To relieve pain in lumbar osteochondrosis, analgesics are used in tablets or injections, the second option is better, because it is more effective. To relieve the inflammatory process, anti-inflammatory drugs (non-steroidal) are prescribed. Muscle spasms that occur simultaneously with pain are eliminated by muscle relaxants. Chondroprotectors are used to restore damaged cartilage tissue.
All these drugs sometimes do not have the desired effect, because damage prevents the drug from penetrating to the site of action.
Restraints are used to relieve acute attacks of pain. Only experts should carry it out.
An appropriate analgesic is injected into the gap between the spinous process with a long needle. After such a procedure, the pain disappears quickly, but for a while, because there is no therapeutic effect.
Effective use of local complex means - ointments, gels. They have an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, warming effect, many topical preparations contain chondroprotectors. These drugs, when used correctly and combined with massage, are quite effective.
Physiotherapy procedures
In combination with drug treatment for lumbar osteochondrosis, physiotherapeutic procedures are used - balneotherapy, laser and magnetotherapy, treatment with weak current, light and vibration. They practically have no side effects and contraindications.
Alternative Methods
More and more alternative (non-traditional) methods are used simultaneously with traditional treatment - hirudotherapy, acupuncture, bee stings, manual therapy. These methods provide long-awaited relief, but some of them have contraindications, so consultation with the attending physician is required.
In addition to all the above treatment methods, physical therapy helps to overcome this disease. Properly distributed load with the required intensity will help restore blood circulation in the damaged area, form or strengthen the muscle corset, and thus unload the spine.
In the treatment of osteochondrosis, it is important to combine treatment methods correctly, first of all, acute pain attacks are relieved, then the inflammatory process, and only when the acute period of the disease ends, non-traditional methods and physical exercises can be performed. used.
The Yoga and Pilates complex has proven to be very good as a rehabilitation program for spinal diseases.
Hernia of the lumbar spine
Against the background of untreated or neglected osteochondrosis in the lumbar region, hernias very often develop - a disease in which, due to insufficient physical activity or excessive load, nutrition of the disc tissue occurs, its strength decreases and, as a result, the disc ruptures. The process of destruction can last for years and go unnoticed all this time, but with one unsuccessful movement, the mechanism starts, and all the symptoms begin to appear one after another.
General symptoms and course of the disease
Symptoms of a lumbar spinal hernia include decreased tendon reflexes, pain of varying intensity, muscle weakness, and numbness in the legs. Pain with a hernia does not always occur, back pain is possible, which gradually spreads towards the pinched nerve.
Distortion of the body is a characteristic sign of a lumbar hernia. This phenomenon happens involuntarily, because the body needs to find the most comfortable position where the pain is minimal. In the course of a severe and rapidly progressive disease, the result may be paralysis of the lower leg (partial or complete). This phenomenon is usually accompanied by disturbances in the function of the abdominal organs, especially the intestines and bladder.
The clinical manifestations of lumbosacral zone hernia are expressed in a constant increase in pain and its intensification during certain physical exercises (heavy lifting, bending, sharp strong muscle tension, coughing), dull aching pain with localization at one point that does not go far, direction of pain in the partback or legs, or numbness in the area.
Diagnosis of lumbar spinal hernia
It is difficult to diagnose a hernia visually or with the symptoms described by the patient alone. To more accurately determine the presence of the disease, several methods are used that will help determine the exact location of the disease. Computed tomography, nuclear magnetic resonance and radiography - thanks to these methods, the doctor will be able to visually determine the location of the pathologically altered vertebrae and see the deformed disc.
To determine the severity of the disease and its consequences, the doctor uses several tests: raising the straightened leg, tendon reflexes, sensitivity (response) of the leg at all levels (from the toes to the hip joint) to several types of stimuli - pain, vibration and temperature.
Treatment Methods
Depending on the severity and condition of the patient, different hernia treatment methods are used. In case of exacerbation, first of all, it is necessary to immediately limit motor activity until bed rest and relieve pain with medication. After 5-7 days, when the acute period ends and the pain has subsided, drug treatment is supplemented with other rehabilitation procedures (massage, physiotherapy, physical education).
Medical and conservative treatment of lumbar hernia is the same as osteochondrosis.
Surgery
In cases of severe disease and the presence of many serious consequences, surgical treatment is advised.
Indications for surgery:
- hernia resorption - part of the disc damaged by the hernia enters the spinal canal;
- dysfunction of all or one organ in the pelvis;
- patency in the spinal canal is impaired (determined by MRI);
- lack of results when using medical and conservative treatment methods for three or more months;
- inflammation of the sciatic nerve.
Surgical treatment of hernia is now carried out with the help of prudent and minimally invasive endoscopic operations.
The laser reconstruction method consists of evaporating the fluid from the protruding nucleus pulposus using a laser. Thanks to this, the nerve root is "released", that is, its compression is eliminated. But this type of intervention has some contraindications, these are early operations on the spine, spondylolisthesis, spondyloarthritis, impaired patency of the spinal canal (stenosis) and protrusion of the nucleus pulposus into the canal.
To remove the damaged part of the intervertebral disc, a percutaneous discectomy method is used. Evaporation and removal of damaged tissue is done with a needle inserted through the skin.
In cases when it is impossible to restore the damaged disc in any way, starting with medication and ending with minimally invasive operations, or all methods used do not bring any results, the defective disc is replaced with a prosthesis.
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of the disease, special exercises are prescribed. The exercise complex should be developed by a specialist individually for each patient and must contain exercises for muscle stretching, tension and light aerobic exercise.
With a hernia of the lumbar spine, doctors recommend wearing a special fixing belt. Externally, it resembles a capsule, its width is about 30 cm, it is attached to the body with Velcro and has several degrees of rigidity.
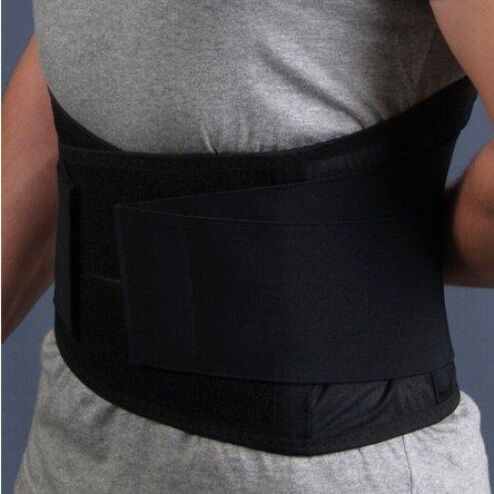
This product is needed to distribute the load evenly (from the diseased area to the healthy one) and relieve stress (unloading). The injured spinal segment with continuous wearing of the belt is corrected and returned to its anatomical position.
Lumbodynia with radicular syndrome
Against the background of osteochondrosis and hernia of the lumbar spine, as a result, lumbago develops - lumbar back pain (acute paroxysmal pain). This is the most "simple" scenario. Since hernia and osteochondrosis are characterized by frequent deformation and prolapse of damaged discs and displacement of the spinal column, there is a violation of nearby nerve roots, which is called radicular syndrome.
It is strengthened by a violation of the vein, which causes edema of the (soft) tissue and congestion. The symptoms of lumbodynia with radicular syndrome are similar to the symptoms of lumbar hernia (acute shooting pain radiating downwards, loss of sensitivity and impaired reflexes), and since this is the consequence, the cause must initially be treated with an integrated approach, otherwise the deformity threatens.
Sciatica
Another consequence of hernia and osteochondrosis is inflammation of the sciatic nerve - sciatica and accompanying pain radiating to the legs or back. Despite the ability to clearly determine the place of "pain", the reason lies in the spine.
Sciatica is not an independent disease, this term refers to some symptoms that accompany certain diseases of the spine. The sensation of pain can be different, in some cases it is just a slight discomfort when staying in the same position is not very comfortable for a long time, and sometimes the pain leads to loss of consciousness and analgesics in this case do not help.
For effective treatment, it is not enough to diagnose sciatica or lumbago; in any case, it is necessary to carry out a full comprehensive examination by various specialists and identify the cause precisely, because it is a provoking factor. With the removal of only a few symptoms, the likelihood of progression of the underlying disease and the appearance of many complications increases. Taking care of your health, early detection of problems and prompt treatment are the keys to good health.
















